What is Feudalism?

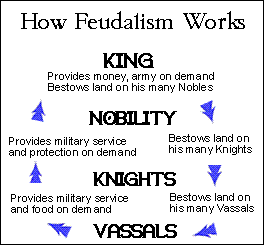
Feudalism is a decentralized sociopolitical structure in which a weak monarchy attempts to control the lands of the realm through reciprocal agreements with regional leaders. This type of social structure was established and used during Medieval Europe, revolving around the three key concepts of lord, vassal, and fief.
The king and queen were at the top of the hierarchy. Nobles were vassals of the king. Knights served the nobles in exchange of land. Peasants, however, were sometimes not included in the feudalism because they owned no land, but they worked on lands owned by the nobles. Knights treated and protected nobles as lord. Then the nobles gave the knights a land called fief.
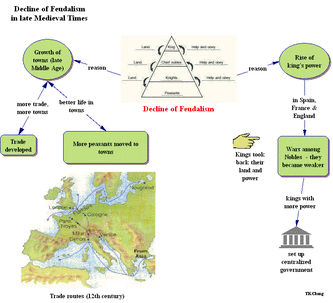
After the year of 1000, many small towns became large cities. This was a result from a rapid growth of population. Improvements of technology also helped farmers to produce more food than before. When food increased, trade also increased. This led to the decline of feudalism. Knights started to call for money instead of land in exchange for their services. Serfs and peasants left their manor for a better life in town. Kings with increased power
The king and queen were at the top of the hierarchy. Nobles were vassals of the king. Knights served the nobles in exchange of land. Peasants, however, were sometimes not included in the feudalism because they owned no land, but they worked on lands owned by the nobles. Knights treated and protected nobles as lord. Then the nobles gave the knights a land called fief.
After the year of 1000, many small towns became large cities. This was a result from a rapid growth of population. Improvements of technology also helped farmers to produce more food than before. When food increased, trade also increased. This led to the decline of feudalism. Knights started to call for money instead of land in exchange for their services. Serfs and peasants left their manor for a better life in town. Kings with increased power